ex09_point_cloud
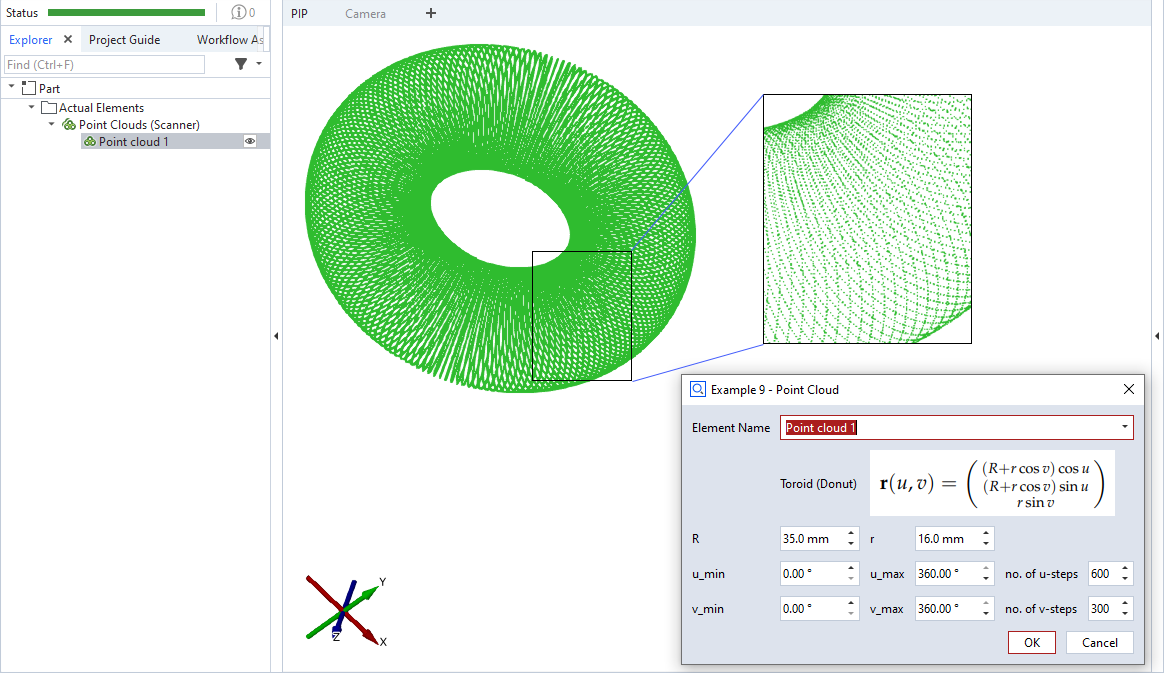
This is an example for a scripted ‘point cloud’ element. A parametric function is used to define the points, in this case the surface points of a torus. np.arange() is used to iterate from u_min to u_max and from v_min to v_max with non-integer step sizes. The step sizes u_steps and v_steps define the point density.
Note
Please see offset_point_v2.md for a complete scripted elements example with detailed description.
Source code excerpt
1def dialog(context, params):
2 #[...]
3
4def calculation(context, params):
5 valid_results = False
6
7 # Calculating all available stages
8 for stage in context.stages:
9 # Access element properties with error handling
10 try:
11 # Creating a list of points using a parametric curve function:
12 # / (R+r*cos(v))*cos(u) \
13 # P(u, v) = | (R+r*cos(v))*sin(u) |
14 # \ r*sin(v) /
15 # with u in [u_min...u_max], v in [v_min...v_max]
16 points = []
17 for u in np.arange(params['u_min'], params['u_max'], (params['u_max'] - params['u_min']) / params['u_steps']):
18 for v in np.arange(params['v_min'], params['v_max'], (params['v_max'] - params['v_min']) / params['v_steps']):
19 p = gom.Vec3d(
20 (params['R'] + params['r'] * math.cos(v * math.pi)) * math.cos(u * math.pi),
21 (params['R'] + params['r'] * math.cos(v * math.pi)) * math.sin(u * math.pi),
22 params['r'] * math.sin(v * math.pi)
23 )
24 points.append(p)
25
26 context.result[stage] = {'points': points}
27 context.data[stage] = {"ude_mykey": "Example 9"}
28 except Exception as error:
29 context.error[stage] = str(error)
30 else:
31 valid_results = True
32 return valid_results